Autoimmune disorders occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. These disorders can range from mild to severe and can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, and organs. While genetic factors play a role in the development of autoimmune disorders, research has also shown that diet can play a significant role in either exacerbating or mitigating the symptoms of these conditions.
The Role of Inflammation
Inflammation is a key factor in the development and progression of autoimmune disorders. Certain foods can trigger inflammation in the body, leading to heightened immune responses and worsening symptoms of autoimmune conditions. Foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and trans fats have been shown to increase inflammation in the body, while foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties.
The Gut Microbiome Connection
The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of bacteria that reside in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in the functioning of the immune system. Research has shown that imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to the development of autoimmune disorders. Diet plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, with a diet high in fiber and fermented foods promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing inflammation in the gut.
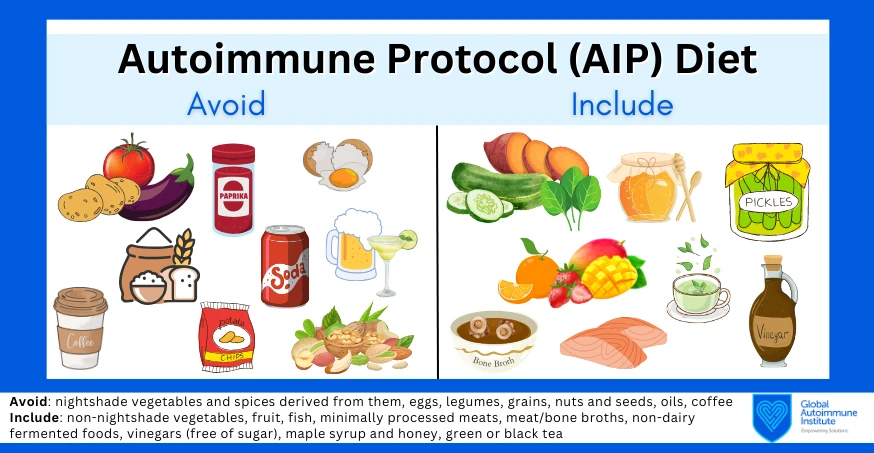
Common Dietary Triggers
While the specific dietary triggers for autoimmune disorders can vary from person to person, there are some common foods that have been shown to exacerbate symptoms in many individuals. Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, is a common trigger for autoimmune conditions such as celiac disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Dairy products, nightshade vegetables, and processed foods containing artificial additives are also known to trigger inflammation in the body.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Autoimmune Disorders
An anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce symptoms and flare-ups in individuals with autoimmune disorders. This diet typically includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help reduce inflammation in the body. Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, can promote a healthy gut microbiome and support immune function.
Individualized Approach to Diet
It’s important for individuals with autoimmune disorders to work with a healthcare provider or dietitian to develop an individualized approach to diet. Some individuals may benefit from eliminating specific trigger foods, such as gluten or dairy, from their diet, while others may need to focus on balancing their macronutrient intake or supplementing with certain nutrients. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers and monitor the effects of dietary changes on symptoms.
Conclusion
Diet plays a significant role in the development and management of autoimmune disorders. By following an anti-inflammatory diet, individuals with autoimmune conditions can help reduce inflammation in the body, support a healthy gut microbiome, and improve overall immune function. Working with a healthcare provider or dietitian to develop an individualized approach to diet can help individuals with autoimmune disorders manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Remember, what you put into your body can have a profound impact on your health, especially when it comes to autoimmune disorders. By making informed dietary choices and taking a proactive approach to managing your condition, you can improve your overall well-being and reduce the severity of your symptoms.

